In our contemporary society, the reliance on a consistent and uninterrupted power supply has become paramount. Disruptions due to power outages can significantly impact our daily lives, ranging from minor inconveniences in residential settings to critical operational failures in industrial and commercial sectors. Amidst this backdrop, the generator set, often referred to as a genset, has emerged as an indispensable piece of equipment. Fundamentally, a genset is a portable or stationary system that converts mechanical energy into electrical power. These versatile machines find extensive applications across various environments, from providing backup power for homes during unexpected outages to serving as the primary power source in remote locations devoid of grid connectivity.
This article aims to offer a more detailed exploration of generator sets, encompassing their essential components, operational principles, numerous advantages, and the wide spectrum of their applications, drawing from the insights provided by Mengjia Group.
Delving into the Core Components of a Generator Set
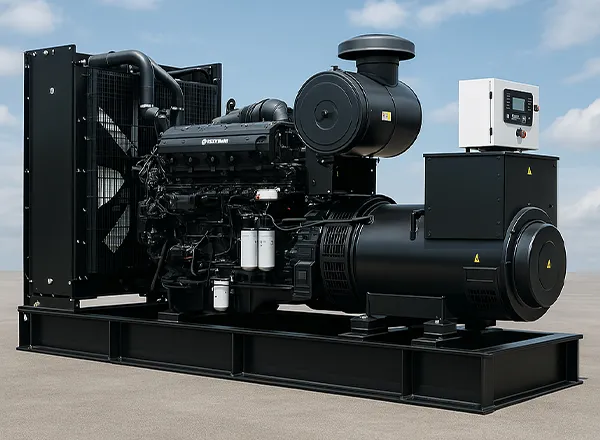
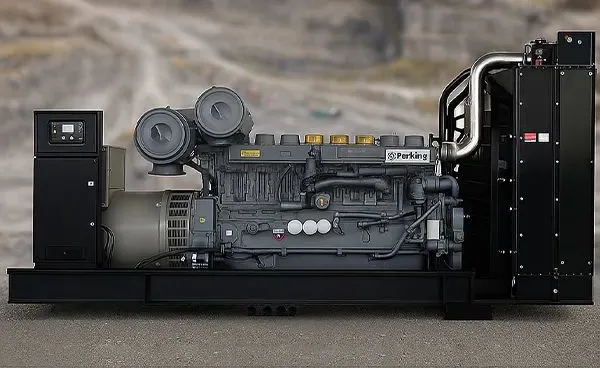
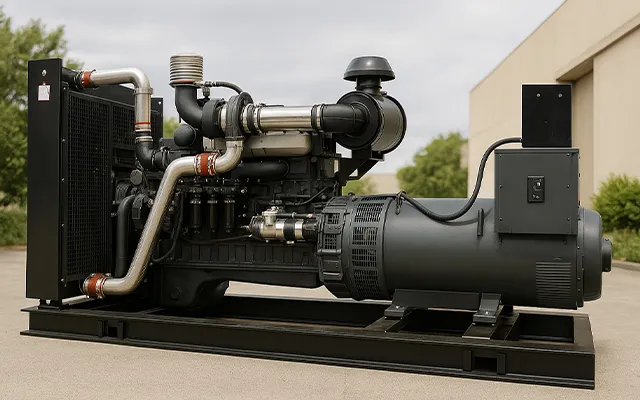
At the heart of every generator set lies a series of crucial components working in concert to produce electrical energy.
- Engine:The engine acts as the prime mover, converting chemical energy, typically from fuel, into mechanical energy through internal combustion. The type of engine employed can vary, with common options including diesel, gasoline, natural gas, or propane engines, the selection often depending on the intended application and the availability of a particular fuel source. The robustness and quality of the engine are critical in ensuring a reliable power source over extended periods.
- Alternator:The alternator is the pivotal component responsible for transforming the mechanical energy generated by the engine into electrical energy. This process involves a rotor (the moving part) and a stator (the stationary part), both containing copper wire windings. The interaction between the magnetic field of the rotor and the stator induces an electromotive force (EMF), ultimately producing the desired voltage and frequency output that aligns with local power grid standards.
- Voltage Regulator:To ensure a stable and consistent power supply, the voltage regulator plays a vital role. This mechanism regulates and maintains a steady voltage output, thereby safeguarding sensitive electronic devices from potential damage caused by fluctuations in voltage.
- Cooling System:The operation of a generator set generates a significant amount of heat. An efficient cooling system is therefore essential to maintain the engine temperature at an optimal level. Typically comprising a radiator and cooling fans, this system prevents overheating and ensures the smooth and prolonged performance of the engine.
- Control Panel:The control panel serves as the user interface for monitoring and controlling the generator set’s functions. It typically displays critical operating parameters such as voltage, frequency, fuel level, and operating hours. Advanced control panels may also incorporate features like automatic start/stop functionality, load sharing capabilities, and safety shutdown systems.
Exploring the Different Types of Generator Sets and Their Applications
The diverse power needs across various sectors have led to the development of different types of generator sets, each tailored for specific applications. The selection of the appropriate generator type hinges on factors such as the required wattage and the preferred fuel source.
- Portable Generator Sets:Characterized by their compact size and lightweight design, portable generators are engineered for convenient use in a variety of scenarios. Their primary applications include providing backup power during emergencies, powering equipment for camping or outdoor events, and supplying electricity for tools and construction equipment on smaller sites. These sets generally offer power outputs ranging from a few hundred to several thousand watts.
- Backup Generators:Designed as standby power sources, backup generators are engineered to automatically start within seconds of a utility power outage. They are ideally suited for ensuring uninterrupted power for homes and larger buildings such as hospitals and data centers, where power continuity is critical.
- Inverter Generators:Inverter generators utilize advanced technology to invert electricity, resulting in a cleaner and safer power output that is particularly suitable for sensitive electronic equipment.
- It’s worth noting that most generators produce alternating current (AC), which is well-suited for powering a wide range of equipment in construction sites, homes, and buildings. Direct current (DC), on the other hand, which flows in only one direction, is typically used for large-scale operations like subway systems.
The Operational Mechanics of Generator Sets
A generator set functions through a fundamental process of energy conversion. It comprises a prime mover (usually an engine) and an alternator. The engine initiates the process by converting the chemical energy stored in the fuel into mechanical energy. This mechanical energy is then harnessed to rotate the rotor within the alternator. The alternator, consisting of the rotor and the stator, then converts this mechanical energy into electrical energy. This conversion occurs through electromagnetic induction, where the rotation of the magnetic field between the rotor and stator induces a voltage on the alternator stator. When this voltage is connected to an electrical load, current flows, and the generator produces electricity. Generator sets can be fueled by various sources, including diesel, natural gas, or solar power. Diesel generator sets, in particular, will operate continuously as long as there is a sufficient fuel supply, offering the advantage of portability and power provision in off-grid locations.
The Multifaceted Benefits of Utilizing Generator Sets
Investing in a well-constructed, industrial-grade genset yields numerous advantages for businesses and industries alike. These benefits extend beyond simply providing backup power.
- Reliability:Generators offer a dependable source of power when the primary grid fails, ensuring business continuity and operational stability.
- Fuel Efficiency:Modern generator sets are designed with fuel efficiency in mind, optimizing operational costs.
- Scalable Design:Many generator systems offer scalable designs, allowing businesses to adjust their power capacity as their needs evolve.
- Robust Construction:Industrial-quality gensets are built to withstand demanding operating conditions, ensuring longevity and consistent performance.
- Automatic or Manual Paralleling:Advanced systems can be configured for paralleling, allowing multiple generators to work together to meet larger power demands or provide redundancy.
- Automatic Loading Control:This feature optimizes the generator’s performance based on the connected load, enhancing efficiency and preventing overload.
- Local or Remote Operation:Depending on the model and configuration, generators can be operated and monitored locally or remotely, offering greater flexibility and control.
- Low Emissions:Modern generators are increasingly designed with technologies to minimize emissions, adhering to environmental regulations.
- Increased Productivity:By providing backup power, businesses can avoid costly downtime and maintain full operational capacity, which is particularly crucial for industries relying on constant power for technology and equipment.
- Enhanced Security:During power outages, generators ensure the continued operation of security systems, surveillance cameras, and lighting, deterring potential threats and protecting assets.
- Improved Reputation and Customer Satisfaction:Businesses that can maintain operations during power outages are perceived as reliable and trustworthy, fostering customer loyalty and positive referrals.
The Wide-Ranging Applications and Significance of Generator Sets
Generator sets play a critical role across numerous sectors, addressing diverse power needs.
- Emergency Backup Power:Providing backup power during unexpected utility outages is a primary application. This ensures the continuity of essential services in healthcare facilities, commercial establishments, and residential complexes.
- Remote Areas and Construction Sites:In locations with limited or no grid access, generators are a lifeline, powering lighting, tools, machinery, and other essential equipment. Construction sites heavily rely on generators for uninterrupted operations.
- Agriculture and Farming:Generators are vital for irrigation systems, refrigeration units, milking machines, and other farm equipment, maintaining productivity and mitigating the impact of power fluctuations, especially in remote agricultural areas.
- Telecommunications:Ensuring the uninterrupted functioning of telecommunications networks is crucial. Generators provide a reliable power source in areas prone to outages or with limited grid access, guaranteeing seamless connectivity.
- Events and Outdoor Activities:From concerts and festivals to camping trips, generators supply power for lighting, audio systems, food trucks, and other equipment, enhancing the experience without dependence on the local grid.
Conclusion: The Enduring Importance of Generator Sets
Generator sets have evolved into an indispensable element of our modern infrastructure, guaranteeing a consistent power supply in critical situations, remote areas, and a multitude of other applications. As our dependence on electricity continues to grow across virtually every facet of our lives, the significance of generator sets will only amplify, serving as a crucial backup power solution when it is needed most. Mengjia Group emphasizes the quality and reliability of their generator sets through thorough inspection, repair, and verification processes. With a wide selection available, they aim to provide the optimal model to meet diverse operational needs. Recognizing that power requirements vary significantly based on geographical and industrial factors, Mengjia Group encourages potential customers to contact them to discuss their specific needs.